How to Care for Pet Turtles at Home: Complete Guide
“Complete Guide to Caring for Pet Turtles: Learn how to set up the perfect turtle habitat, feed your turtle a balanced diet, maintain health, and enrich their environment for a happy and thriving pet.”
Introduction
Caring for pet turtles is a long-term responsibility that requires correct knowledge and daily attention. Many beginners think turtles are easy pets, but understanding how to care for pet turtles properly is essential for their health, growth, and long life. Proper pet turtle care includes the right tank setup, balanced diet, clean habitat, and regular health monitoring. This complete guide will explain everything you need to know about how to care for pet turtles in a simple and effective way.

Turtle Habitat Setup
Aquarium and Tank Size
A well-designed habitat is the first step in caring for pet turtles. Aquatic turtles need 10 gallons of water per inch of shell. For example, a 5-inch Red-Eared Slider needs a 50-gallon tank minimum. Land turtles require secure enclosures with ample room to roam, dig, and bask.
Indoor habitats should be well-ventilated with a secure lid to prevent escapes. Outdoor pens must be predator-proof, with shaded and moist areas that allow turtles to exhibit natural behaviors. A proper habitat reduces stress and supports healthy growth.
Water Quality and Filtration
Clean water is essential in pet turtle care. Use a high-quality filter to maintain water quality and reduce infection risk. Maintain species-appropriate water temperatures (most aquatic turtles thrive at 75–85°F / 24–29°C). Perform weekly partial water changes to prevent bacterial buildup.
Heating and Lighting
Turtles need UVB lighting to metabolize calcium and prevent metabolic bone disease. Basking areas should reach 85–90°F (29–32°C). Land turtles may require less water heating but need a warm basking spot. Timed lighting creates a natural day-night cycle, essential for healthy turtle behavior.
Substrate and Decoration
Use safe substrates such as reptile carpet, soil, sand, or coconut fiber. Avoid small gravel that can be ingested. Include rocks, logs, plants, and hiding spots to encourage climbing, basking, and exploring. Enriched habitats reduce stress and support mental and physical health.
Turtle Tank Setup (Most Important Step)
A correct turtle tank setup is the foundation of turtle health. The tank should be large enough to allow swimming and basking.
Ideal Turtle Tank Setup Includes:
Tank Size: Minimum 40 gallons for one turtle
Water Filter: Strong filter to keep water clean
Basking Area: Dry platform with heat lamp
UVB Lighting: Essential for shell and bone health
Water Temperature: 75–80°F
Basking Temperature: 90–95°F
A poor turtle tank setup can lead to stress, shell rot, and weak immunity.
Turtle Habitat Setup (Indoor & Outdoor)
Proper turtle habitat setup plays a key role in caring for pet turtles. The habitat should closely match their natural environment.
Turtle Habitat Setup Tips:
Use smooth rocks and hiding areas
Avoid sharp or toxic decorations
Maintain clean water at all times
Follow a proper day and night lighting cycle
A well-planned turtle habitat setup supports natural behavior and helps owners learn how to care for pet turtles more effectively.
Turtle Diet & Nutrition
Balanced turtle diet and nutrition is essential for shell strength, immunity, and growth. Feeding the wrong food is one of the most common mistakes in caring for pet turtles.
Healthy Turtle Diet Includes:
High-quality turtle pellets
Leafy greens (collard greens, romaine lettuce)
Vegetables (carrots, squash)
Protein sources (worms, insects, small fish in moderation)
Calcium supplements for shell health
Proper turtle diet and nutrition is a major part of how to care for pet turtles long-term.

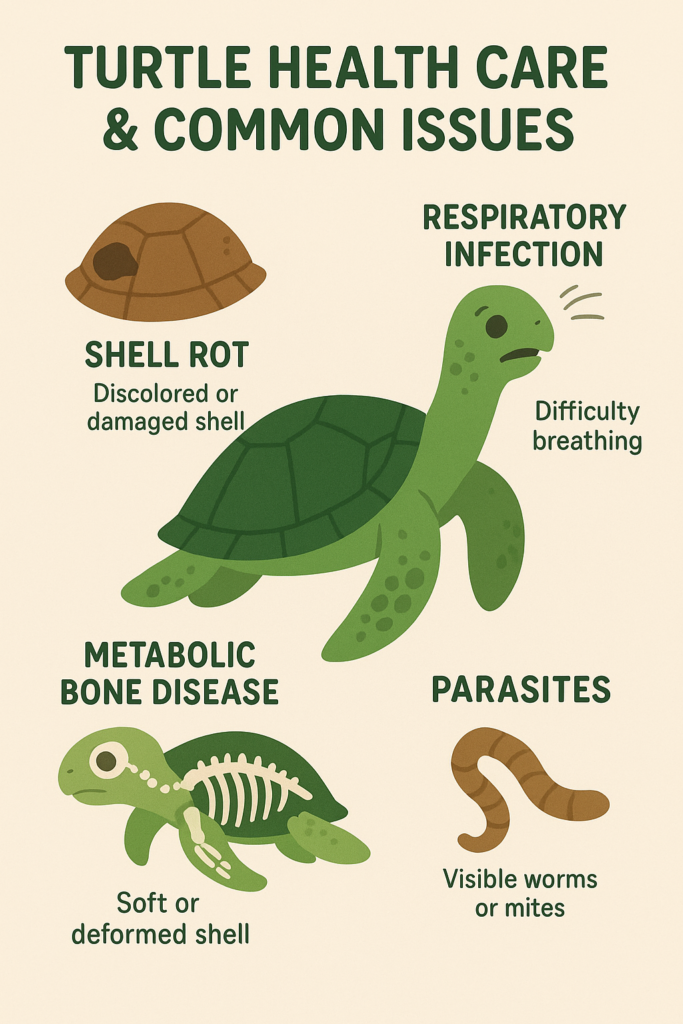
Turtle Health Care & Common Issues
Signs of a Healthy Turtle
Healthy turtles have bright, clear eyes, smooth shells, active swimming or walking, and a strong appetite. Observe for proper shedding and skin condition. Similarly, just as proper monitoring and care are essential for turtles, following the right Diet for Cats with Feline Upper Respiratory Infections is crucial to support recovery, strengthen immunity, and maintain overall health in affected cats.
Common Health Problems
Respiratory infections: Poor water quality or low temperatures; symptoms include wheezing and lethargy.
Shell deformities: Soft shells or pyramiding from inadequate UVB or diet.
Parasites: Check feces; consult a vet if abnormal.
Obesity: From overfeeding or lack of exercise.
Preventive Care
Maintain clean water and regulated temperatures.
Provide UVB lighting and calcium supplements.
Conduct regular health checks with a reptile vet.
Observe turtles daily for unusual behavior or physical changes.
Turtle Behavior & Enrichment
Common Behaviors
Basking: Important for digestion and thermoregulation.
Exploring: Indicates curiosity and activity.
Hiding: Can signal stress or molting.
Digging: Normal in land turtles.
Swimming: Active swimming shows good health.
Enrichment Tips
Include rocks, logs, floating platforms, and plants.
Rotate decorations for stimulation.
Hide food to encourage natural foraging.
Use safe interactive toys for aquatic turtles.
Seasonal & Handling Tips
Adjust lighting, heating, and diet for seasonal changes
Outdoor turtles may need sheltered areas or indoor relocation in winter
Handle turtles gently; avoid lifting by limbs or tail
Wash hands before and after handling to prevent bacteria spread
Common Mistakes in Caring for Pet Turtles
Many new owners struggle with how to care for pet turtles due to common mistakes:
Using small tanks
Skipping UVB lighting
Poor water quality
Unbalanced diet
Excessive handling
Avoiding these mistakes improves pet turtle care and increases lifespan.
Final Thought
Nutrition is another critical component. Turtles are omnivorous or herbivorous depending on their species, and feeding them the wrong diet can lead to deficiencies or obesity. Fresh vegetables, high-quality turtle pellets, and occasional protein sources, along with vitamin supplements, can help ensure they live a long and healthy life.
Equally important is routine observation and healthcare. Turtles may hide signs of illness until conditions become serious, so monitoring their behavior, shell condition, and appetite regularly is essential. Establishing a relationship with a reptile-savvy veterinarian can make a significant difference in the long-term health of your pe
Following this complete guide to caring for pet turtles ensures your turtle thrives in a safe, clean, and enriched environment. Proper habitat, diet, health checks, and enrichment prevent common issues and promote longevity.
Turtles are intelligent, fascinating pets that can live for decades. This turtle care guide helps you understand your turtle’s needs, maintain health, and enjoy a rewarding pet experience. Observe your turtle daily, adjust care seasonally, and provide a balanced environment to keep your turtle happy and thriving.
FAQ: Caring for Pet Turtles
1. How do I set up a proper habitat for my pet turtle?
Setting up a proper habitat is the first step in caring for pet turtles. For aquatic turtles, choose a tank large enough to provide 10 gallons of water per inch of turtle shell. Include a basking area with a heat lamp and UVB lighting to support calcium metabolism and prevent shell deformities. The tank should have a secure lid to prevent escapes, and the water should be kept clean with a reliable filtration system.
Land turtles, like Box Turtles or Tortoises, require enclosures with enough space to roam, dig, and bask. Include hiding spots, logs, and plants to mimic a natural environment. Ensure proper temperature and humidity for the species you own. Outdoor enclosures must be predator-proof and weather-resistant, with shaded areas and moist zones. A well-planned habitat reduces stress, encourages natural behaviors, and improves overall health and longevity.
2. What should I feed my turtle?
Diet is crucial for turtle health. Most turtles are omnivores, so a balanced diet includes leafy greens, vegetables, and occasional protein such as insects, worms, or small fish. Species-specific dietary needs are important: Red-Eared Sliders thrive on aquatic plants and occasional protein, while Box Turtles enjoy a mix of fruits, vegetables, and insects.
Calcium supplements are essential for strong shell and bone development, and UVB lighting is necessary for proper calcium absorption. Fruits can be offered occasionally, but avoid citrus and sugary foods. Feeding a varied diet ensures turtles get all the necessary nutrients and helps prevent shell deformities, obesity, and vitamin deficiencies.
3. How often should I feed my turtle?
Feeding frequency depends on age and species. Young turtles typically eat once or twice daily to support rapid growth, while adult turtles may only need feeding every 2–3 days. Monitor how much your turtle consumes to avoid overfeeding, which can cause obesity or poor water quality.
For aquatic turtles, remove uneaten food promptly to prevent bacterial growth and water contamination. Providing the right portion size ensures your turtle remains healthy, maintains a normal growth rate, and avoids digestive issues. Overfeeding protein, especially for young turtles, can lead to shell pyramiding or soft shells.
4. How can I tell if my turtle is healthy?
Healthy turtles display several key signs. Their eyes should be clear and bright, and their shell firm, smooth, and free of discoloration. They should be active, swimming or walking normally, and show a strong appetite.
Observe your turtle’s behavior daily. Lethargy, unusual hiding, or decreased appetite may indicate stress or illness. Skin discoloration, swelling, or irregular shedding are warning signs of potential health issues. Regular monitoring and timely intervention help prevent minor problems from becoming serious, ensuring long-term turtle wellness.
5. What are common health problems in turtles?
Turtles are prone to several health issues. Respiratory infections often occur due to poor water quality, low temperatures, or drafts. Symptoms include wheezing, open-mouth breathing, and lethargy.
Shell deformities, such as soft shells or pyramiding, are usually caused by inadequate UVB exposure, insufficient calcium, or overfeeding protein. Parasites may affect turtles internally or externally, and obesity can result from overfeeding or lack of exercise. Regular health checks, proper diet, and clean environments reduce these risks and help maintain a long and healthy life.

Pingback: Nutrition and Diet for Cats with Feline Upper Respiratory Infections (URIs) – Complete Guide