Fatty Liver Treatment - How to Reverse Fatty Liver Naturally & Medically
Discover effective fatty liver treatment options, including natural remedies, lifestyle changes, and medical solutions. Learn how to reduce liver fat and improve liver health safe
Fatty liver affects millions worldwide, caused by excess fat in liver cells. This guide covers 7 proven fatty liver treatment methods, including diet changes, exercise routines, natural remedies, and medical options. Learn the main causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies to reverse liver fat effectively and maintain a healthy, fully functioning liver.
1. What Is Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver refers to the accumulation of excess fat in the liver cells. There are two main types:
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Caused by poor diet, obesity, or metabolic issues.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): Caused by excessive alcohol consumption.
If left untreated, fatty liver can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which may cause liver scarring and failure.
1. Understanding Fatty Liver
Fatty liver happens when fat makes up more than 5–10% of your liver weight. There are two main types:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Caused by metabolic factors, obesity, diabetes, and poor diet.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): Resulting from excessive alcohol intake, leading to fat accumulation and liver inflammation.
Early-stage fatty liver is often silent, with no visible symptoms. However, untreated fatty liver can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver failure.
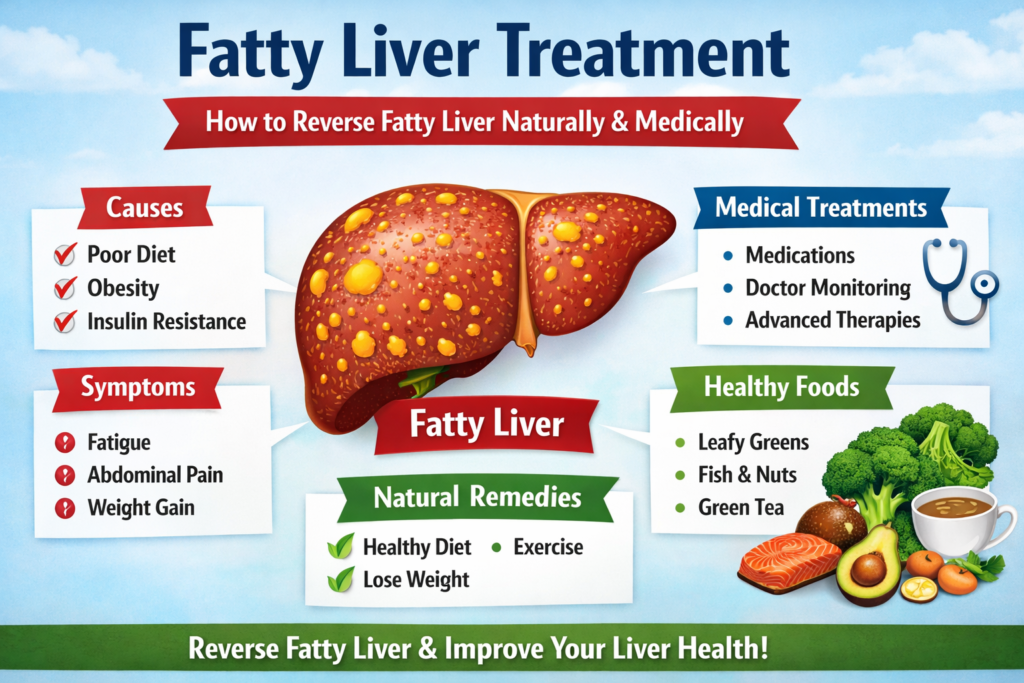
2. Causes of Fatty Liver
Understanding the root causes is critical for effective fatty liver treatment:
a. Poor Diet – High intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, fried foods, and unhealthy fats.
b. Obesity & Excess Weight – Central obesity increases fat deposition in liver cells.
c. Insulin Resistance & Diabetes – Leads to impaired fat metabolism in the liver.
d. Sedentary Lifestyle – Lack of exercise reduces fat burning, causing fat accumulation.
e. Excessive Alcohol – Alcoholic fatty liver develops from repeated alcohol-induced liver injury.
f. Genetic Predisposition – Some people are more susceptible due to genetics.
3. Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is often asymptomatic in the early stages, but some signs may include:
Fatigue and weakness
Abdominal discomfort or mild pain in the upper right abdomen
Unexplained weight gain or loss
Enlarged liver detected during checkups
High cholesterol or triglycerides
Early detection allows for more effective fatty liver treatment, reducing the risk of complications.
4. Fatty Liver Treatment: Lifestyle & Home Remedies
Lifestyle changes are the first and most effective approach to treat fatty liver:
a. Healthy Diet
Focus on vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Reduce sugar, processed foods, and saturated fats.
Include liver-friendly foods like leafy greens, walnuts, garlic, and fatty fish.
b. Weight Management
Aim for a 5–10% reduction in body weight.
Weight loss reduces fat in liver cells, improves insulin sensitivity, and lowers inflammation.
c. Regular Exercise
At least 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily (walking, swimming, or cycling).
Exercise burns liver fat and supports overall metabolic health.
d. Limit Alcohol Intake
Alcohol contributes to liver inflammation and fat buildup.
Reducing or eliminating alcohol can prevent further liver damage.
e. Control Diabetes & Cholesterol
Manage blood sugar and cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and medications if prescribed.
f. Natural Remedies & Supplements
Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants that improve liver function.
Coffee: Moderate intake reduces liver fat and inflammation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, help reduce liver fat.
Milk Thistle: Supports liver detoxification and regeneration.
5. Medical Fatty Liver Treatment
If lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, medical interventions may be necessary:
a. Prescription Medications
Medications may target insulin resistance, high cholesterol, or liver inflammation.
Vitamin E has been shown to improve liver function in some NAFLD patients.
b. Regular Monitoring
Blood tests, ultrasounds, or FibroScan can track liver fat and fibrosis.
Early monitoring helps adjust treatment plans effectively.
c. Advanced Treatments
In severe cases, patients with NASH or cirrhosis may require specialized therapies or liver transplantation.
6. Diet Plan for Fatty Liver Treatment
A sample liver-friendly diet includes:
Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and chia seeds
Lunch: Grilled salmon with quinoa and steamed vegetables
Snack: Walnuts or an apple
Dinner: Stir-fried chicken with broccoli and brown rice
Hydration: Plenty of water and green tea

7. Tips to Maintain a Healthy Liver After Treatment
Consistent Exercise: Maintain at least 30–45 mins daily.
Balanced Diet: Avoid processed sugar and saturated fats.
Regular Checkups: Monitor liver enzymes and fat levels.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can worsen fatty liver; meditation and yoga help.
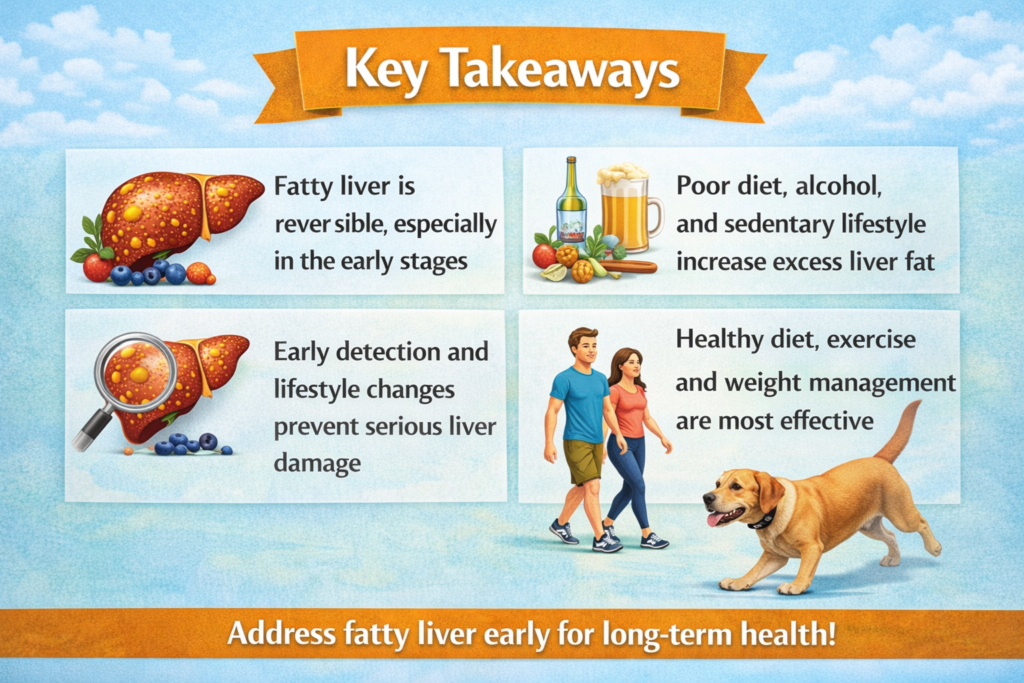
8. Key Takeaways
Fatty liver is reversible, especially in the early stages.
Lifestyle changes remain the most effective treatment.
Medical treatments are available if liver inflammation is severe.
Healthy diet, exercise, weight management, and alcohol reduction are crucial.
Early detection is essential for long-term liver health.
FAQs Fatty Liver Treatment
Q1: What is fatty liver disease?
A: Fatty liver disease occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver. It can be caused by poor diet, obesity, insulin resistance, or excessive alcohol. Early detection is crucial as it can lead to liver inflammation or cirrhosis if left untreated.
Q2: What are the main causes of fatty liver?
A: Common causes include obesity, high sugar and fat intake, insulin resistance, diabetes, sedentary lifestyle, and excessive alcohol consumption. Genetic factors can also increase the risk of fat accumulation in the liver, making prevention and lifestyle changes essential.
Q3: What are the symptoms of fatty liver?
A: Fatty liver often shows no early symptoms but may cause fatigue, mild abdominal discomfort, weight changes, and enlarged liver. Blood tests or ultrasounds can detect liver fat, allowing early intervention through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
Q4: How is fatty liver treated naturally?
A: Natural fatty liver treatment includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, weight management, reducing alcohol intake, and incorporating liver-friendly foods like leafy greens, walnuts, fatty fish, and antioxidants such as green tea. These changes help reduce liver fat and inflammation.
Q5: Are there medical treatments for fatty liver?
A: Yes, doctors may prescribe medications to manage diabetes, cholesterol, or liver inflammation. Vitamin E or other therapies may be recommended in NAFLD cases. Severe liver damage may require specialized treatments or monitoring to prevent progression to cirrhosis.
Q6: Can fatty liver be reversed?
A: Yes, early-stage fatty liver is largely reversible with proper lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and weight loss. Reducing alcohol consumption and managing underlying conditions like diabetes also significantly improves liver health and prevents further fat accumulation.
Q7: What foods should be avoided in fatty liver?
A: Avoid sugary drinks, fried foods, processed snacks, high-fat dairy, and excessive red meat. These foods contribute to fat accumulation in the liver. Instead, focus on vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean protein for effective fatty liver treatment.
Q8: How long does it take to improve fatty liver?
A: Improvement varies by individual, but consistent lifestyle changes like diet and exercise can reduce liver fat within 3–6 months. Regular monitoring and adherence to fatty liver treatment recommendations accelerate results and prevent progression.
